Artificial Intelligence Adoption May Have Turned a Corner
Mister Roboto has arrived in the form of a formidable artificial intelligence (AI) frenzy. Rather stagnant yet steady for years, AI adoption spiked dramatically in the between mid-2023 to now according to McKinsey. We see this from AI gaining momentum in permeating various industry sectors, including healthcare, finance, transportation, and cybersecurity, with applications ranging from predictive analytics to autonomous systems.
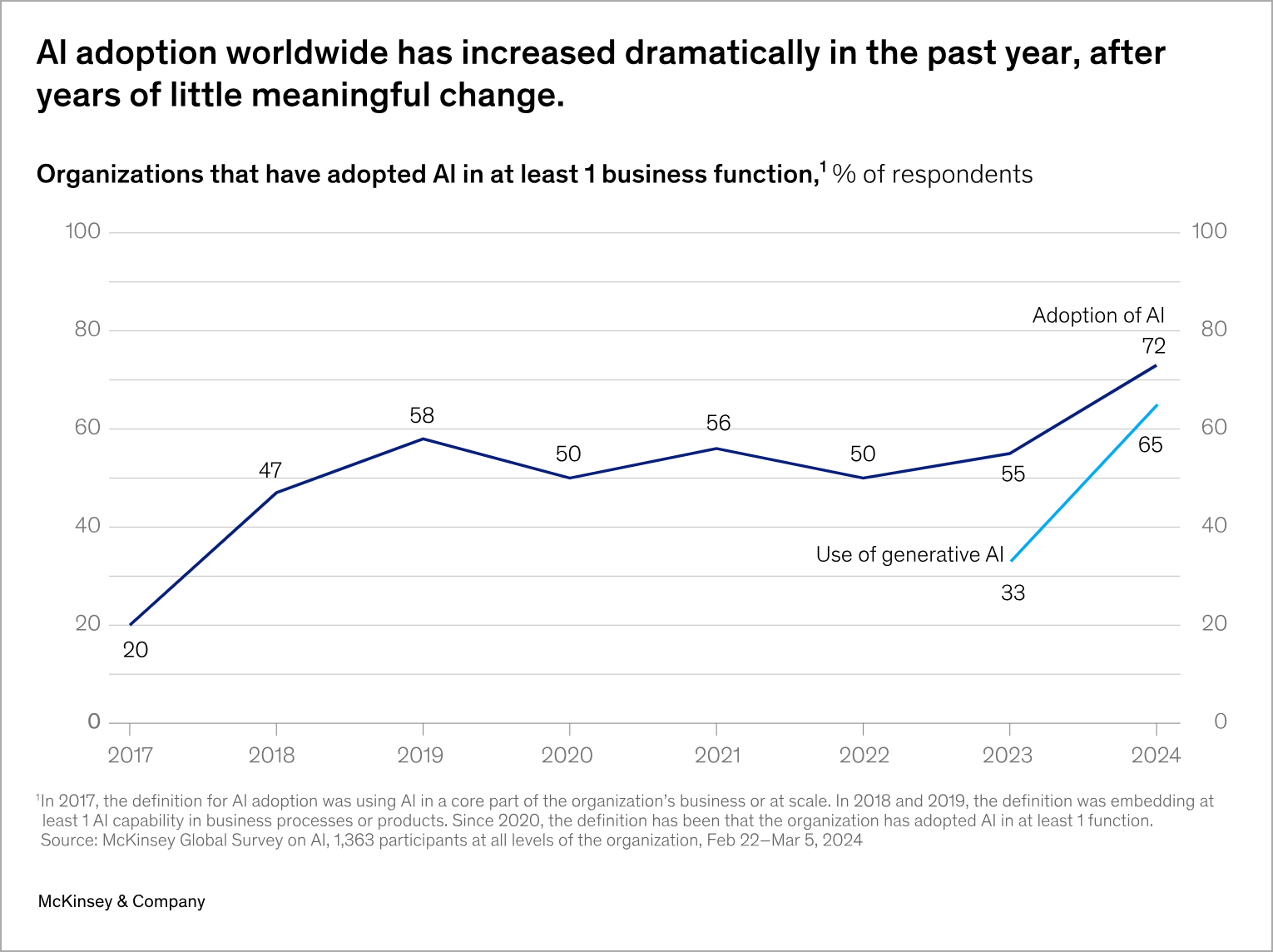
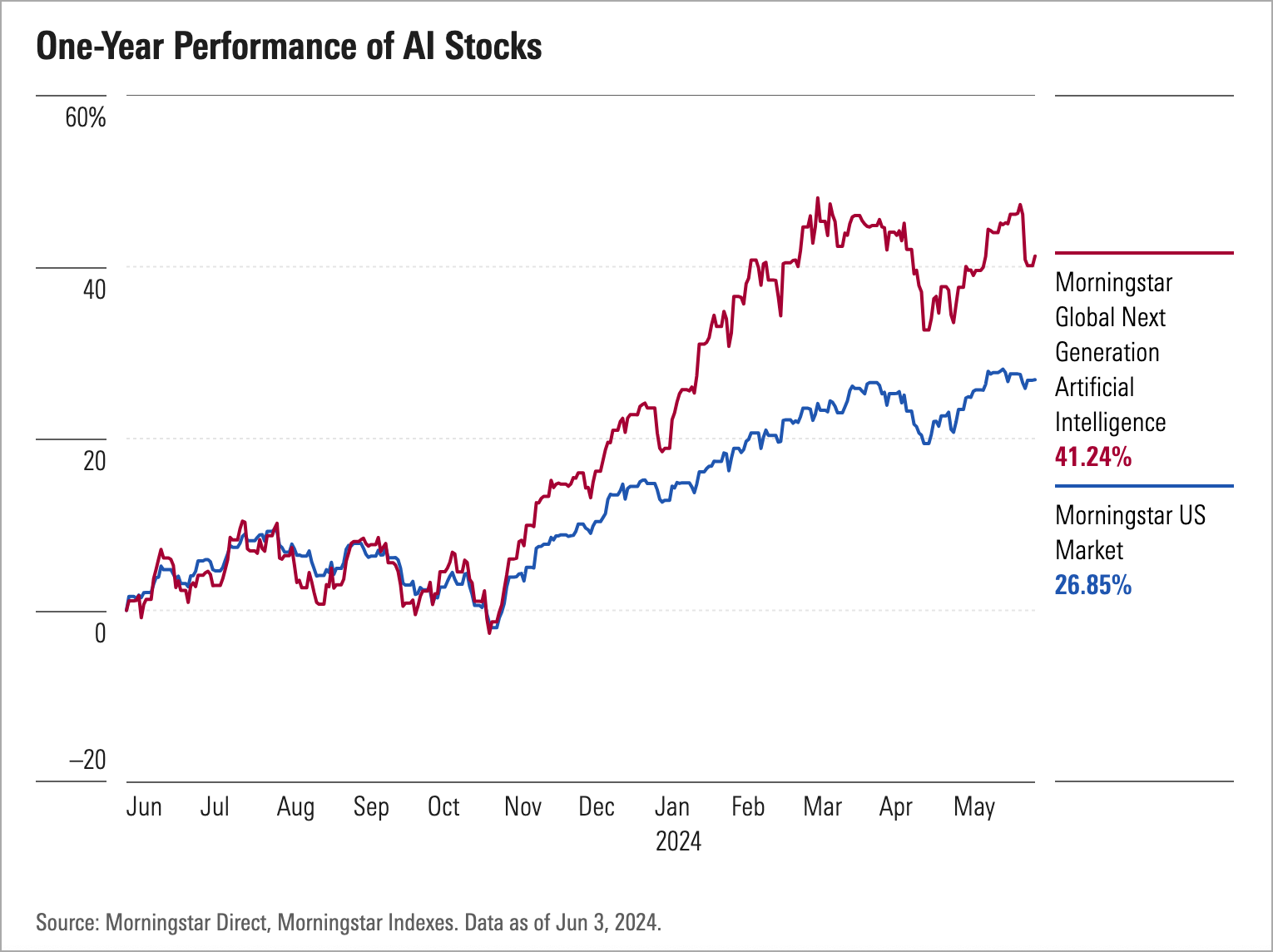
Identifying promising sectors early can yield substantial returns for investors, both venture capitalists and corporations. A one-year performance of Morningstar AI Technologies saw a sizeable rise over the standard Morningstar U.S. market. The hype is turning into revenue, as the metrics explain.
Consequently, tech giants like Meta and Google parent Alphabet have also seen their stocks surge in the first half of the year as the companies leveraged their positions in the industry and their ability to meet the capital-intensive needs of AI advancement to lead developments in the space.
AI Investment Considerations: VCs versus Corporate Buyers
Venture capital and corporate investor preferences in AI stocks vary based on risk appetite, investment strategies, and confidence in the future of AI technologies. However, understanding the contrasting priorities of these variables by the two investor groups provides valuable insights into the AI investment landscape.
VC Priorities in AI Startup Investments
Venture capitalists specialize in spotting nascent AI ventures with game-changing technologies and business models primed for rapid expansion. Their investment strategy centers on three core pillars: explosive growth potential, cutting-edge innovation, and proven market demand. This approach allows VCs to construct a varied portfolio aimed at generating substantial long-term returns. Let’s delve deeper into the key factors that guide VC decision-making in AI investments:
1. Technological AI Innovation
VCs are drawn to technologies that have the power to disrupt existing markets or create entirely new ones. They seek unique and proprietary algorithms or methodologies that provide startups with a sustainable competitive edge. Intellectual property, including patents and trade secrets, is highly valued as it safeguards the technology from competitors.
2. Market Growth Potential
The question “Will this product or service sell?” is paramount. VCs assess an AI solution’s market viability by evaluating the company’s potential to not just survive but flourish in the marketplace. They look for evidence of product-market fit, which can be quantifiably determined by how well the startup’s offering addresses market needs and solves critical problems. Early indicators of customer adoption, such as user metrics, sales figures, or successful pilot programs, are seen as positive signs of market readiness.
3. Exit Potential
VCs meticulously assess a startup’s exit potential as a crucial factor in their investment decisions. They evaluate the likelihood of various lucrative outcomes, including the possibility of acquisition by a larger company, which can provide substantial returns. Additionally, VCs consider the startup’s capability to eventually go public through an IPO, offering another avenue for significant financial gains. Beyond these exit strategies, VCs also scrutinize the startup’s market positioning, looking for companies with the potential to either dominate a niche market or expand to become a major player in a broader industry. This comprehensive evaluation of exit scenarios and market potential helps VCs gauge the long-term value and return prospects of their investments in AI startups.
4. Portfolio Diversification
Venture capitalists employ a strategic approach to risk management by constructing diversified portfolios of AI investments. This strategy involves spreading investments across various sectors, such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous systems, among others. By diversifying across different industries and applications of AI technology, VCs aim to balance their exposure to market-specific risks and capitalize on opportunities in multiple high-growth areas. This approach not only helps to mitigate potential losses from underperforming investments but also increases the chances of capturing significant returns from breakthrough successes in different AI domains.
5. Cost-Effective Scalability
Venture capitalists seek assurance that a business can expand quickly with minimal additional expenses. For example, a strong and adaptable technological framework capable of managing higher demands. Additionally, a business model structure that enables revenue growth without a corresponding increase in costs, such as the Software as a Service (SaaS) model.
6. Team Expertise
VCs place significant emphasis on the founding team’s capabilities, expertise, and vision. They typically seek teams that can effectively translate their vision into reality, demonstrating the ability to set and achieve milestones, adapt to market changes, and drive the company forward. Those with deep domain knowledge of the specific sector or problem space their AI technology addresses, ensuring a nuanced understanding of market needs. While not always mandatory, a track record of previous entrepreneurial success is highly valued. It suggests the team’s ability to navigate the challenges of building and scaling a startup.
7. Overall Risk Assessment
Venture capitalists engage in a thorough risk assessment process as an integral part of their AI investment strategy. This multifaceted evaluation encompasses several key risk factors. Technical risk is scrutinized to determine the feasibility of developing and scaling the proposed AI technology, considering potential challenges in implementation and innovation. Market risk is carefully analyzed, focusing on the uncertainties surrounding market acceptance, competitive landscape, and the startup’s ability to capture and retain market share. Additionally, VCs pay close attention to regulatory risk, particularly in the AI sector, where legal and ethical considerations can significantly impact a startup’s trajectory. This includes assessing potential hurdles in data privacy, algorithmic bias, and industry-specific regulations.
Corporate Buyers’ Strategies in AI Technology Acquisitions
Corporate buyers corporate buyers are increasingly targeting AI acquisitions that resonate with their strategic goals. Acquisition or investment positions that may enhance product offerings, accelerating innovation, or expand market reach. Acquiring AI technologies enables companies to gain a competitive edge, drive operational efficiency, and capitalize on emerging trends in AI. Here’s a closer look at how these acquisitions align with various corporate objectives:
1. Enhancing Product Offerings
Corporate buyers leverage AI acquisitions to significantly upgrade their existing product lines. By integrating advanced AI-driven features such as predictive analytics, natural language processing, or machine learning algorithms, companies can dramatically enhance the value proposition of their offerings. This strategic move not only makes products more attractive to customers but also allows businesses to stay competitive in rapidly evolving markets. The integration of AI capabilities can transform ordinary products into smart, adaptive solutions that better meet customer needs and expectations, ultimately driving increased sales and market share.
2. Accelerating Innovation
AI acquisitions serve as a catalyst for innovation within corporate structures. By bringing in AI startups or technologies, companies inject fresh talent, novel ideas, and cutting-edge capabilities into their innovation pipelines. This infusion of AI expertise enables corporations to navigate the fast-paced tech landscape more effectively, facilitating quicker development and deployment of state-of-the-art solutions. The synergy between acquired AI capabilities and existing corporate resources can lead to breakthrough innovations, helping companies maintain a leading position in their respective industries and potentially disrupt markets with revolutionary products or services.
3. Expanding Market Reach
AI technologies offer corporations powerful tools to break into new market segments and geographical regions. For instance, advanced natural language processing (NLP) capabilities can enable companies to offer their services in multiple languages, effectively expanding their global footprint. AI-driven market analysis and predictive modeling can also help identify untapped market opportunities, allowing companies to tailor their offerings to diverse customer bases. This expansion not only increases revenue streams but also diversifies the company’s market presence, reducing dependence on any single market or region.
4. Gaining a Competitive Edge
The integration of AI technologies provides companies with a significant competitive advantage. By leveraging AI-powered predictive analytics, businesses can make more informed, data-driven decisions, staying ahead of market trends and customer preferences. Machine learning algorithms can optimize various aspects of operations, from supply chain management to customer service and personalized marketing efforts. This enhanced operational intelligence and efficiency allow companies to outperform competitors, respond more quickly to market changes, and deliver superior customer experiences, solidifying their market position.
5. Driving Operational Efficiency
AI acquisitions play a crucial role in streamlining business processes and driving operational efficiency. Technologies such as robotic process automation (RPA) can automate routine, repetitive tasks, freeing up human resources for more strategic activities. Machine learning algorithms can optimize resource allocation, improve forecasting accuracy, and enhance decision-making processes. These AI-driven efficiencies lead to significant cost savings, improved productivity, and better resource utilization across the organization, ultimately contributing to increased profitability and competitiveness.
6. Capitalizing on Emerging Trends
By acquiring AI companies or technologies, corporations position themselves at the forefront of emerging technological trends. This strategic move allows them to tap into future advancements and potentially disrupt traditional industries. For example, acquiring a company specializing in AI for healthcare could open doors to the rapidly growing fields of personalized medicine or telehealth. Such acquisitions not only provide immediate technological capabilities but also offer long-term strategic advantages, allowing companies to shape industry trends and establish themselves as leaders in emerging markets.
7. Intellectual Property
Acquiring AI companies provides corporations with valuable intellectual property assets, including patents, proprietary algorithms, and other innovative technologies. This bolsters the company’s market position by creating significant barriers to entry for competitors. A strong IP portfolio not only protects the company’s innovations but also opens up new revenue streams through licensing opportunities. Additionally, it enhances the company’s attractiveness to investors and partners, potentially leading to further growth opportunities and solidifying the corporation’s position as an innovation leader in its industry.
AI Investment Considerations Visualized
While there may be some overlap in these considerations, investors generally focus more on financial returns and market potential, while corporations prioritize strategic fit, integration, and the ability to enhance their competitive position in the market.

![Investing in AI: Contrasting Priorities of VCs and Corporate Buyers [Infographic] Depositphotos 160926688 XL scaled](https://www.socialmarketingfella.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Depositphotos_160926688_XL-1000x600.jpg)

![Investing in AI: Contrasting Priorities of VCs and Corporate Buyers [Infographic] Week26 2024 AI 1 1 scaled](https://www.socialmarketingfella.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/06/Week26-2024-AI-1-1-150x150.jpg)
![Investing in AI: Contrasting Priorities of VCs and Corporate Buyers [Infographic] Big Tech AI 1](https://www.socialmarketingfella.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/Big-Tech-AI-1-150x150.png)